[et_pb_section fullwidth=”on” specialty=”off” transparent_background=”off” background_color=”#64cbae” inner_shadow=”off” parallax=”off” parallax_method=”off” background_image=”https://prc3.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/background02.jpg”][et_pb_fullwidth_header admin_label=”Fullwidth Header” title=”Strategic Prevention Framework” background_layout=”dark” text_orientation=”left” /][/et_pb_section][et_pb_section][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”4_4″][et_pb_text admin_label=”Text” background_layout=”light” text_orientation=”left”]
[box]
Quick Facts
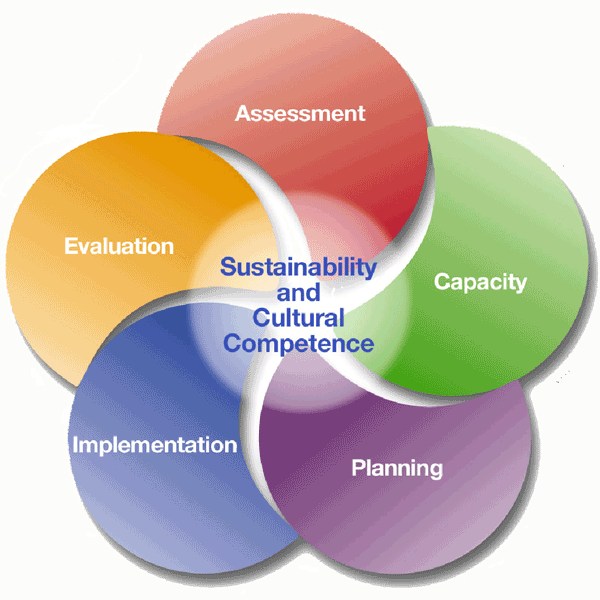
The Five Steps of SAMHSA’s Strategic Prevention Framework
- Step #1 – Profile population needs, resources and readiness to address needs and gaps.
- Step #2 – Mobilize and/or build capacity to address needs.
- Step #3 – Develop a Comprehensive Strategic Plan.
- Step #4 – Implement evidence-based prevention programs, policies and practices.
- Step #5 – Monitor, evaluate, and sustain.
[/box]
Overview
The five steps that comprise the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration’s (SAMHSA) Strategic Prevention Framework (SPF) will enable states and communities to build the infrastructure necessary for effective and sustainable prevention. Each step contains key milestones and products that are essential to the validity of the process. The SPF is conceived of in systemic terms and reflects a public health, or community-based, approach to delivering effective prevention.
This Information Brief examines each of the five steps used to promote understanding of the requirements to successfully implement the strategic prevention framework. A matrix of milestones and products for each of the five SPF steps can be found on the second page of this brief. Carnevale Associates, LLC will discuss the relationship between the SPF and other best practice prevention processes in a future Information Brief.
Step #1: Assessment
Assessment involves the collection of data to define problems within a geographic area. Assessment also involves mobilizing key stakeholders to collect the needed data and foster the SPF process. Part of this mobilization, and a key component of SAMHSA’s SPF State Incentive Grant program, is the creation of an epidemiological workgroup. The epidemiological workgroup should spearhead the data collection process and is responsible for defining the problems and the underlying factors that will be addressed in Step 4: Implementation. Assessing resources includes assessing cultural competence, identifying service gaps, and identifying the existing prevention infrastructure in the state and/or community. Step 1 also involves an assessment of readiness and leadership to implement policies, programs, and practices.
Step #2: Capacity
Capacity involves the mobilization of resources within a geographic area (state/community). A key aspect of Capacity is convening key stakeholders, coalitions, and service providers to plan and implement sustainable prevention efforts in Steps 3-4 of the SPF. The mobilization of resources includes both financial and organizational resources as well as the creation of partnerships. Readiness, cultural competence, and leadership capacity are addressed and strengthened through education and training. Additionally, Capacity should include a focus on sustainability as well as evaluation capacity.
Step #3: Planning
Planning involves the development of a strategic plan that includes policies, programs, and practices that create a logical, data-driven plan to address the problems identified in Step 1 of the SPF. The planning process produces Strategic Goals, Objectives, and Performance Targets as well as Logic Models and in some cases preliminary Action Plans. In addition to the Strategic Goals, Objectives, and Performance Targets, Step 3 can also involve the selection of evidence based policies, programs, and practices.
Step #4: Implementation
Implementation involves taking action guided by the Strategic Plan created in Strategic Prevention Framework SAMHSA’s Strategic Prevention Framework Information Brief January 2005 © 2005 Carnevale Associates LLC Step 3 of the SPF. If action planning, or the selection of specific policies, programs, and practices, was not part of the planning process in Step 3, it should occur in Step 4. Step 4 also includes the creation of an evaluation plan, the collection of process measure data, and the ongoing monitoring of implementation fidelity.
Step #5: Evaluation
Evaluation involves measuring the impact of the SPF and the implemented programs, policies, and practices. An important part of the process is identifying areas for improvement. Step 5 also emphasizes sustainability since it involves measuring the impact of the implemented policies, programs, and practices. Evaluation also includes reviewing the effectiveness, efficiency, and fidelity of implementation in relation to the Strategic Plan, relevant Action Plans, and measures.
Implications of the SPF
The SPF highlights SAMHSA’s intent to enable states and communities to build prevention infrastructure. SAMHSA is expanding its resources for States and communities beyond programs, policies, and practices to include a focus on infrastructure development and sustainability.
| SPF Step | Key Milestones | Key Products |
| Step 1: Assessment |
|
|
| SPF Step | Key Milestones | Key Products |
| Step 2: Capacity |
|
|
| SPF Step | Key Milestones | Key Products |
| Step 3: Planning |
|
|
| SPF Step | Key Milestones | Key Products |
| Step 4: Implementation |
|
|
| SPF Step | Key Milestones | Key Products |
| Step 5: Evaluation |
|
|
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]
